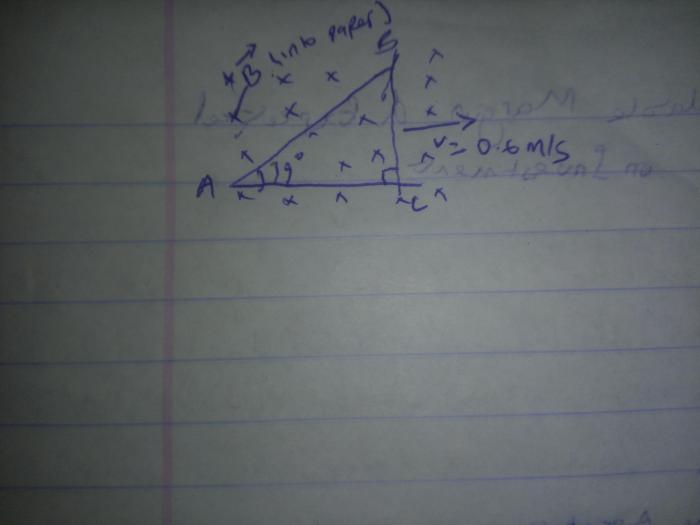
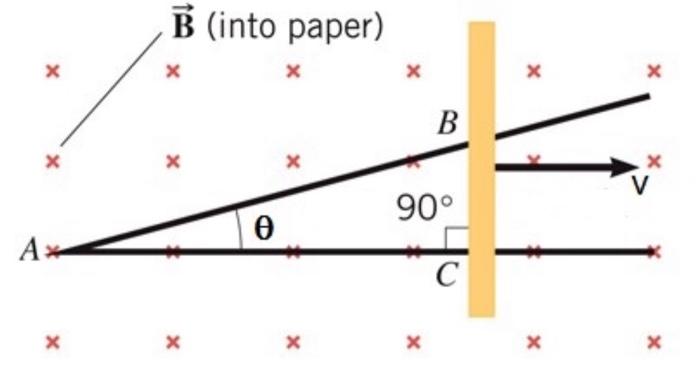
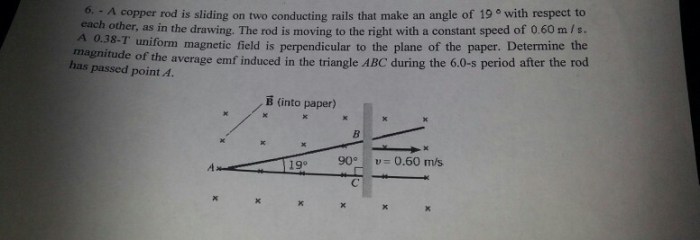
A copper rod is sliding on two conducting rails – A copper rod sliding on two conducting rails embarks on a captivating journey, revealing the intricacies of electromagnetic induction. This phenomenon, where a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor, holds profound implications for our understanding of electricity and its technological applications.
Through an intriguing experiment involving a copper rod gliding along conductive rails, we witness firsthand the interplay between magnetic fields and moving charges. This interaction generates an electric current, providing a tangible demonstration of electromagnetic induction.
Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which an electric current is generated in a conductor when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field.
Concept of Electromagnetic Induction, A copper rod is sliding on two conducting rails
Electromagnetic induction is a fundamental principle of electromagnetism that describes the relationship between electric and magnetic fields. When a conductor is moved through a magnetic field, or when the magnetic field around a conductor changes, an electromotive force (EMF) is induced in the conductor.
This EMF can drive an electric current to flow through the conductor.
The magnitude of the induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the conductor.
Experiment: Copper Rod Sliding on Conducting Rails
The experiment involving a copper rod sliding on conducting rails demonstrates the principle of electromagnetic induction.
The experiment setup consists of a copper rod placed on two parallel conducting rails. A magnet is placed near the rails, creating a magnetic field. When the rod is moved along the rails, it cuts through the magnetic field, inducing an EMF in the rod.
The observations made during the experiment include the following:
- The rod experiences a force that opposes its motion.
- An electric current flows through the rod.
- The magnitude of the induced current is proportional to the speed of the rod.
The significance of this experiment lies in its demonstration of the principle of electromagnetic induction and its application in various practical devices.
Role of Magnetic Fields
Magnetic fields play a crucial role in electromagnetic induction.
Magnetic fields are generated by moving electric charges. When a current flows through a conductor, it creates a magnetic field around the conductor.
In the experiment with the copper rod, the magnetic field generated by the magnet interacts with the moving charges in the rod, inducing an EMF.
Query Resolution: A Copper Rod Is Sliding On Two Conducting Rails
What is electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor.
How does a copper rod sliding on conducting rails demonstrate electromagnetic induction?
As the copper rod moves through the magnetic field, the changing magnetic field induces an electric current in the rod.
What are some applications of electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction is used in a wide range of applications, including generators, transformers, and electric motors.