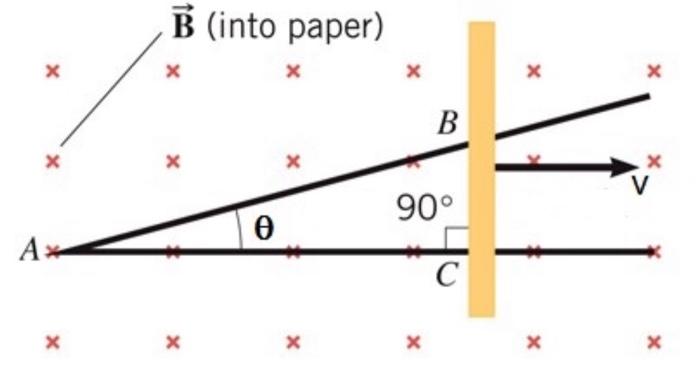
Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of phet charges and charged objects investigation answers, where we unravel the intricate world of static electricity and its profound implications. From the fundamentals of static charges to the dynamic behavior of charged objects, this in-depth exploration delves into the very essence of electrical phenomena, offering a comprehensive understanding that will illuminate your path to mastery.
Prepare to be captivated as we explore the nature of charged objects, deciphering the distinctions between positive and negative charges and witnessing firsthand the intriguing interactions that occur when these charged entities encounter one another. We will delve into the fascinating realm of conductors and insulators, uncovering their unique properties and the crucial role they play in the transfer of electrical charges.
Static Charges: Phet Charges And Charged Objects Investigation Answers
Static charges are electric charges that do not move. They can be either positive or negative. Static charges can be created by friction, contact, or induction.
Examples of static charges in everyday life include the shocks we get from touching a doorknob after walking across a carpet, the cling of clothes after they come out of the dryer, and the sparks that fly when we comb our hair.
Creating Static Charges, Phet charges and charged objects investigation answers
- Friction: When two materials are rubbed together, electrons can be transferred from one material to the other, creating a static charge.
- Contact: When two materials with different electrical charges come into contact, electrons can flow from one material to the other, creating a static charge.
- Induction: When a charged object is brought near an uncharged object, the electrons in the uncharged object will be attracted to or repelled by the charged object, creating a static charge.
Charged Objects

Charged objects are objects that have a net electric charge. They can be either positively charged or negatively charged.
Positively and Negatively Charged Objects
- Positively charged objectshave a net positive charge, meaning they have more protons than electrons.
- Negatively charged objectshave a net negative charge, meaning they have more electrons than protons.
Behavior of Charged Objects
- Charged objects attract each otherif they have opposite charges.
- Charged objects repel each otherif they have the same charge.
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are materials that allow electric charges to flow through them easily. Insulators are materials that do not allow electric charges to flow through them easily.
Examples of Conductors and Insulators
- Conductors: Metals, such as copper, silver, and gold, are good conductors of electricity.
- Insulators: Rubber, plastic, and glass are good insulators of electricity.
Charging by Induction
Charging by induction is a process of charging an object without touching it. When a charged object is brought near an uncharged object, the electrons in the uncharged object will be attracted to or repelled by the charged object, creating a static charge.
Example of Charging by Induction
A simple example of charging by induction is when you rub a balloon on your hair. The friction between the balloon and your hair will cause electrons to be transferred from your hair to the balloon, creating a static charge.
The balloon will then be negatively charged and your hair will be positively charged.
Applications of Charging by Induction
Charging by induction is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Electrostatic spray painting: In electrostatic spray painting, a charged object is used to attract paint particles to the surface being painted, resulting in a more even and consistent coating.
- Laser printers: Laser printers use a charged object to attract toner particles to the paper, creating the printed image.
- Photocopiers: Photocopiers use a charged object to attract toner particles to the paper, creating a copy of the original document.
Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden flow of electric charge between two objects. ESD can occur when two charged objects come into contact, or when a charged object comes into contact with a grounded object.
Causes of Electrostatic Discharge
- Friction: Friction between two materials can create a static charge, which can then be discharged when the materials come into contact.
- Contact: When two charged objects come into contact, the charges can flow from one object to the other, resulting in an ESD.
- Induction: When a charged object is brought near an uncharged object, the electrons in the uncharged object will be attracted to or repelled by the charged object, creating a static charge. This static charge can then be discharged when the uncharged object comes into contact with a grounded object.
Dangers of Electrostatic Discharge
ESD can be dangerous because it can damage electronic equipment. ESD can also cause sparks, which can be a fire hazard.
Applications of Electrostatic Charges
Electrostatic charges have a variety of applications in everyday life, including:
- Dust collection: Electrostatic charges can be used to attract dust particles, making it easier to clean surfaces.
- Air filtration: Electrostatic charges can be used to remove dust and other particles from the air, making it cleaner and healthier to breathe.
- Electrostatic painting: Electrostatic charges can be used to attract paint particles to the surface being painted, resulting in a more even and consistent coating.
- Laser printers: Laser printers use electrostatic charges to attract toner particles to the paper, creating the printed image.
- Photocopiers: Photocopiers use electrostatic charges to attract toner particles to the paper, creating a copy of the original document.
Future Potential of Electrostatic Charges
Electrostatic charges have the potential to be used in a variety of new and innovative applications, including:
- Energy harvesting: Electrostatic charges can be used to generate electricity, which could be used to power small devices or charge batteries.
- Medical applications: Electrostatic charges can be used to deliver drugs to specific parts of the body, or to kill bacteria and viruses.
- Nanotechnology: Electrostatic charges can be used to manipulate and assemble nanoparticles, which could lead to the development of new materials and devices.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of phet charges and charged objects investigations?
Phet charges and charged objects investigations serve as a valuable tool for educators and students alike, providing interactive simulations and visualizations that enhance the understanding of complex electrical concepts.
How can I utilize phet charges and charged objects investigations in my classroom?
Incorporating phet charges and charged objects investigations into your classroom curriculum allows for engaging and interactive learning experiences, fostering a deeper comprehension of electrical phenomena among students.
What are the key takeaways from phet charges and charged objects investigations?
Through phet charges and charged objects investigations, learners gain a profound understanding of static charges, charged objects, conductors, insulators, and electrostatic discharge, equipping them with a solid foundation in electrical principles.