The Periodic Table Review of Terms and Concepts Worksheet provides an in-depth exploration of the fundamental principles and concepts that underpin the organization and properties of elements within the periodic table. This comprehensive resource serves as an invaluable tool for students seeking to deepen their understanding of chemistry and its applications.
The worksheet encompasses a wide range of topics, including the definition and significance of the periodic table, the organization of elements based on atomic number and electron configuration, and the periodic trends in atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity.
Periodic Table Review: Key Concepts
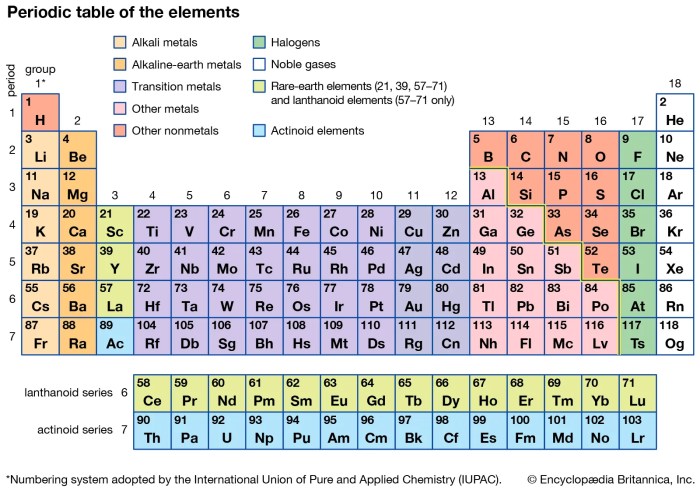
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It is a powerful tool for understanding the chemical behavior of elements and predicting the properties of new elements that have not yet been discovered.
Organization of Elements in the Periodic Table
- Atomic Number:The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Atomic Mass:The weighted average mass of all the isotopes of an element.
- Electron Configuration:The distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals.
Periodic Trends
- Atomic Radius:The distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Generally decreases across a period and increases down a group.
- Ionization Energy:The energy required to remove an electron from an atom. Generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electron Affinity:The energy change when an electron is added to an atom. Generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity:The ability of an atom to attract electrons. Generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Understanding the Periodic Table Worksheet
The periodic table worksheet provides a comprehensive review of the concepts covered in the periodic table unit. It includes sections on the organization of the periodic table, periodic trends, and the properties of elements.
Sections of the Worksheet
- Section 1:Introduction to the Periodic Table
- Section 2:Periodic Trends
- Section 3:Properties of Elements
- Section 4:Applications of the Periodic Table
Tasks in the Worksheet
- Section 1:Define the periodic table and explain its significance.
- Section 2:Identify and explain the periodic trends observed in the worksheet.
- Section 3:Describe the properties and characteristics of representative elements (s-, p-, d-, f-block).
- Section 4:Describe the practical applications of the periodic table in various fields.
Elements and their Properties
The periodic table can be used to organize elements based on their group and period. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Table of Elements
| Group | Period | Element |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Hydrogen |
| 2 | 1 | Helium |
| 13 | 3 | Aluminum |
| 17 | 3 | Chlorine |
| 18 | 3 | Argon |
Properties of Representative Elements
- s-block elements:Alkali metals (Group 1) and alkaline earth metals (Group 2).
- p-block elements:Main-group elements (Groups 13-18).
- d-block elements:Transition metals (Groups 3-12).
- f-block elements:Inner transition metals (Lanthanides and Actinides).
Periodic Trends and Patterns
The periodic table shows clear trends in the properties of elements. These trends can be used to predict the properties of unknown elements.
Observed Periodic Trends, The periodic table review of terms and concepts worksheet
- Atomic Radius:Decreases across a period and increases down a group.
- Ionization Energy:Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electron Affinity:Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity:Increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Exceptions to the Periodic Trends
- Atomic Radius:Helium has a smaller atomic radius than hydrogen.
- Ionization Energy:Boron has a higher ionization energy than beryllium.
Applications of the Periodic Table: The Periodic Table Review Of Terms And Concepts Worksheet
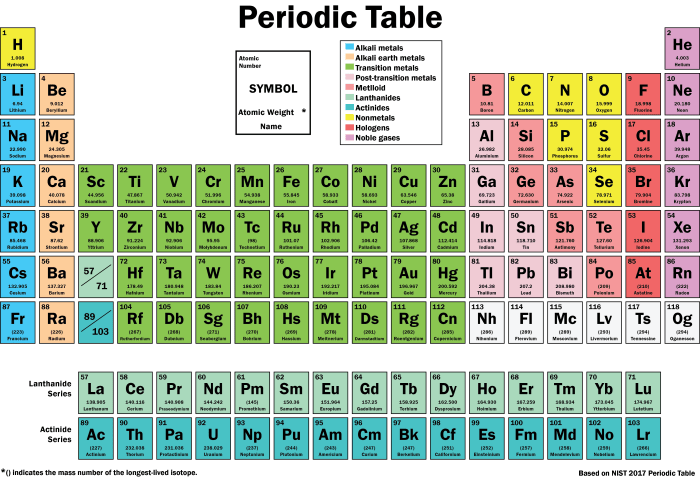
The periodic table is a valuable tool for chemists and other scientists. It can be used to predict the chemical reactivity of elements, guide research, and develop new materials and technologies.
Practical Applications
- Predicting Chemical Reactivity:The periodic table can be used to predict the reactivity of elements based on their position in the table.
- Guiding Research:The periodic table can help researchers identify promising new materials and technologies.
- Developing New Materials and Technologies:The periodic table can be used to design new materials with specific properties.
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of the Periodic Table Review of Terms and Concepts Worksheet?
The worksheet is designed to reinforce students’ understanding of the key concepts and principles related to the periodic table, including the organization of elements, periodic trends, and the properties of elements.
What topics are covered in the worksheet?
The worksheet covers a wide range of topics, including the definition and significance of the periodic table, the organization of elements based on atomic number and electron configuration, and the periodic trends in atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity.
How can the worksheet be used in the classroom?
The worksheet can be used as a review tool, a homework assignment, or as part of a larger unit on the periodic table. It can also be used as a basis for class discussions and activities.
